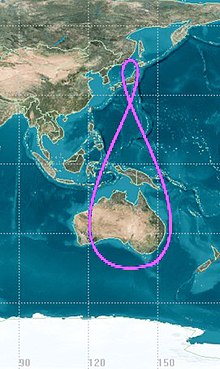
The curved path in space is called an orbit while an orbital period of one sidereal day is known as a geosynchronous orbit. On the other hand, an orbit lying in the plane of the earth’s equator is known as geostationary. Both type of orbits work on the same principle. They are closely related to the force of gravity and perform their tasks on respective ends. The orbit is a unique path in which celestial objects rotate on a specific rate and at the same time, the orbit is also synchronized with the rotation of the earth.
- Difference Between Temple and Shrine
- Difference Between iPad and Android Table
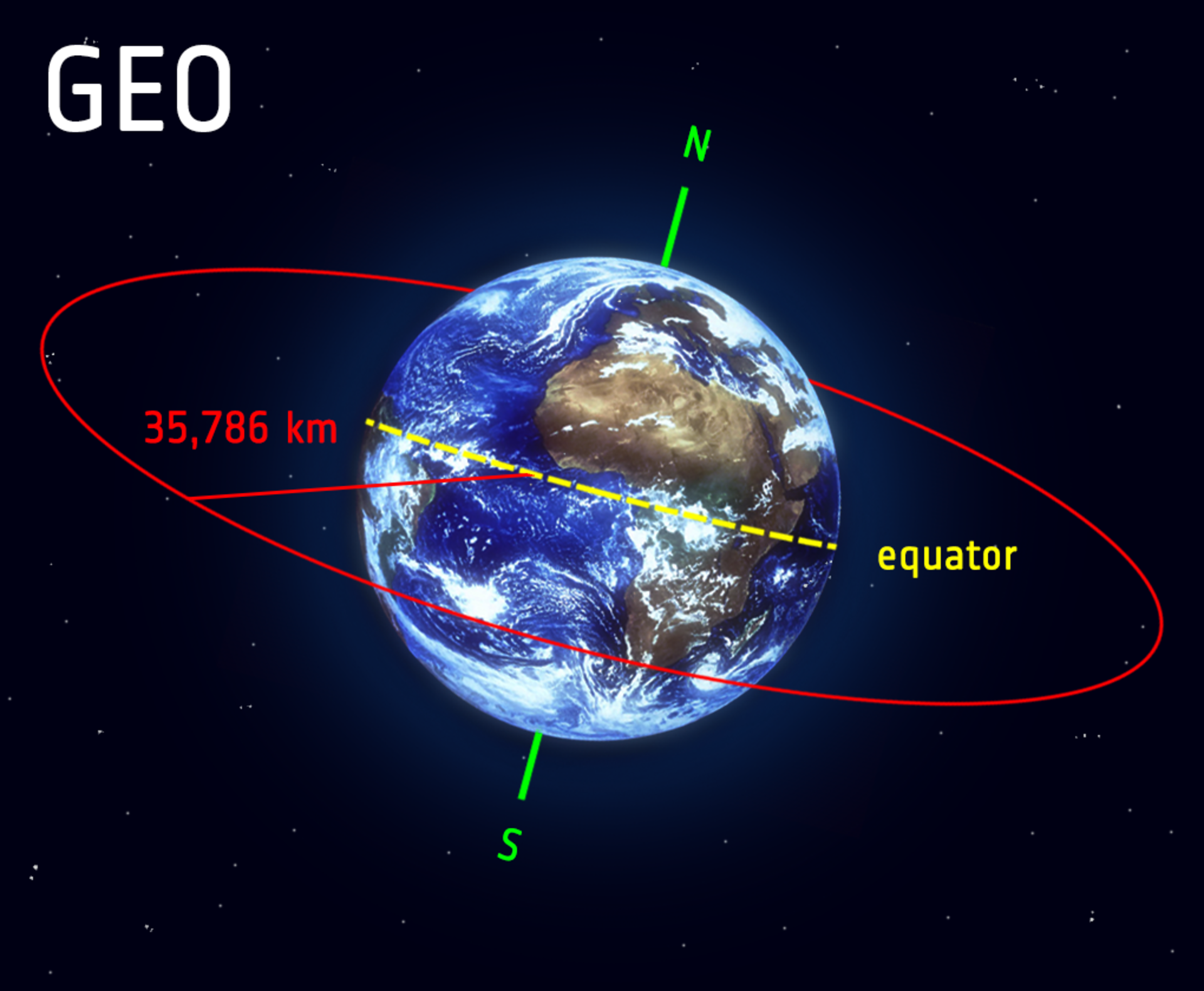
Space stations are located in the geostationary (or geosynchronous) orbit located approximately 23 000 miles in space above the equator. Satellites located between approximately 70° and 145° west longitude can be “seen” from most sites in the continental US except those in the most northerly latitudes. A geosynchronous orbit is a geocentric orbit that has the same orbital period as the sidereal rotation period of the Earth. It has a semi-major axis of 42,164 km (26,200 miles). Geosynchronous Orbits One application of the law of gravity is to figure out how to put a satellite into orbit so that it remains in the same position relative to ground all the time. A satellite in such a position can be used to relay microwave communication signals from one part of the.
Instructions
Geosynchronous Orbit Height
Geosynchronous orbit
Geosynchronous orbit is considered as one sidereal day of an orbital period. Some orbits are smaller in diameter but they move quite fast and complete their circle in a short time. Being smaller in diameter means that a particular orbit it will have faster orbital velocities. Analogously orbits have the same kinds of characteristics as they move very fast to complete a specific cycle. This theory also applies to orbits with a large diameter as it will move slower. Not only will the orbital velocity will be slower but at the same time the orbit cycle will be long. Angular speed of the earth also plays a role for the orbit to complete the circle within a specific time. One sidereal day is roughly 23h 56m and has a semi major axis of 42,164 km.
- Image Courtesy: esc.gsfc.nasa.govGeostationary orbit
Geostationary orbit sits in the plane of the earth’s equator. Geostationary orbit has an additional property when it rotates positions as it moves parallel to the earth. Therefore, it is seen that a specific object always comes above the same point. Many different types of communication satellites are often place in geostationary orbit. Arthur C. Clarke was the first man who advocated this idea that different satellites mainly for telecommunication should be place in geostationary orbit for better performance. This transmission or path works well and now many countries use a geostationary orbit for their satellites. This transmission of geostationary orbit is located 35,786 km, 22,236 miles, above the mean sea level while the Arthur C. Clarke transmission (orbit) is 265,000 km (165,000 miles) long.
- Image Courtesy: blog.apogeeinternet.co.ukDifference between Geosynchronous and Geostationary Orbit
- Difference between Phylum and Class
- Difference Between Monarchy and Democracy
- Difference between Hyena and Jackal
- Difference between Kodiak and Grizzly Bear
- >Education
- >For Students
- >Grades 5-8
- >In the Spotlight
- Send
Student Features
Text Size
| Satellite in Orbit. |
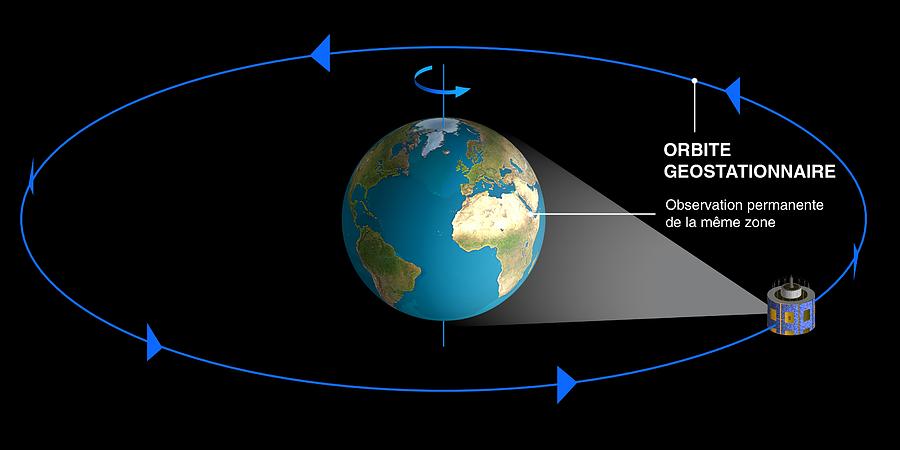
From Earth, a satellite in geosynchronous orbit appears to 'hover' over one spot on the Equator. This helps the receiving dish on the ground. It can get information from the satellite by pointing at just one point in the sky. It doesn't have to move, or 'track,' the satellite across the sky.
The satellite isn't motionless, though. It's in a very high orbit and circles the Earth once a day. This orbit makes the satellite travel at the same rate as the Earth's spin.
Satellites In Geostationary Orbit
There are many satellites currently in geosynchronous orbits. The weather satellite pictures (GIF, 60k) we see on the news come from these satellites. They constantly send pictures and information to receiving dishes on Earth. The GOES weather satellites are an example of this type of satellite. (Visit the GOES Weather Imagery Site). Most cable TV channel signals are also sent around the world with these types of satellites.NASA also uses geosynchronous satellites to send communications and data back and forth between spacecraft, such as the Space Shuttle and the Hubble Space Telescope, and control centers on Earth.